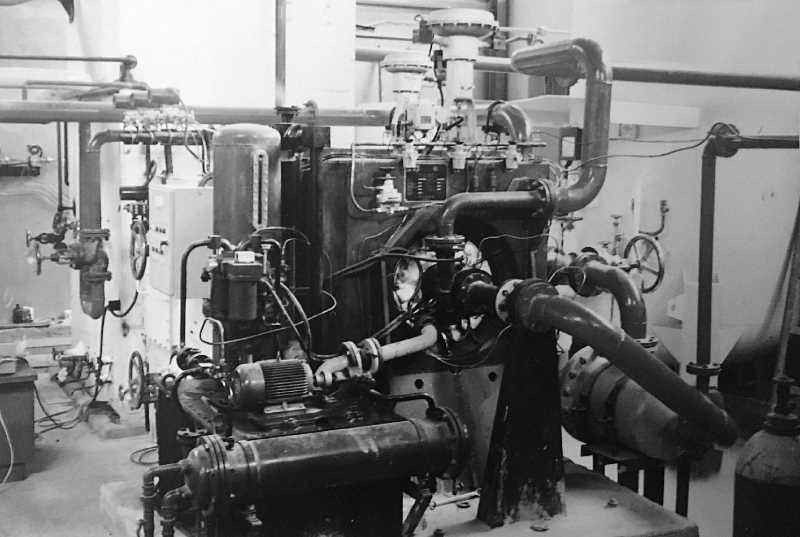
16T / H Coolong Water Consumption Tuobo Expander 250nm3 / H 0.25mpa Pressure
1.description
A turboexpander, also referred to as a turbo-expander or an expansion turbine, is a centrifugal or axial-flow turbine, through which a high-pressure gas is expanded to produce work that is often used to drive a compressor or generator.
Because work is extracted from the expanding high-pressure gas, the expansion is approximated by an isentropic process (i.e., a constant-entropy process), and the low-pressure exhaust gas from the turbine is at a very low temperature, −150 °C or less, depending upon the operating pressure and gas properties. Partial liquefaction of the expanded gas is not uncommon.
Turboexpanders are very widely used as sources of refrigeration in industrial processes such as the extraction of ethane and natural-gas liquids (NGLs) from natural gas,the liquefaction of gases (such as oxygen, nitrogen, helium, argon and krypton)[5][6] and other low-temperature processes.
Turboexpanders currently in operation range in size from about 750 W to about 7.5 MW (1 hp to about 10,000 hp).
2.Power generation
The figure depicts an electric power-generation system that uses a heat source, a cooling medium (air, water or other), a circulating working fluid and a turboexpander. The system can accommodate a wide variety of heat sources such as:
The circulating working fluid (usually an organic compound such as R-134a) is pumped to a high pressure and then vaporized in the evaporator by heat exchange with the available heat source. The resulting high-pressure vapor flows to the turboexpander, where it undergoes an isentropic expansion and exits as a vapor–liquid mixture, which is then condensed into a liquid by heat exchange with the available cooling medium. The condensed liquid is pumped back to the evaporator to complete the cycle.
The system in the figure implements a Rankine cycle as it is used in fossil-fuel power plants, where water is the working fluid and the heat source is derived from the combustion of natural gas, fuel oil or coal used to generate high-pressure steam. The high-pressure steam then undergoes an isentropic expansion in a conventional steam turbine. The steam turbine exhaust steam is next condensed into liquid water, which is then pumped back to steam generator to complete the cycle.
When an organic working fluid such as R-134a is used in the Rankine cycle, the cycle is sometimes referred to as an organic Rankine cycle (ORC).
| condition |
new |
| expander inlet pressure |
0.47mpa |
| booster inlet pressure |
0.1025mpa |
| expander inlet pressure |
0.18mpa |
| booster outlet pressure |
0.22mpa |
| shaft power |
43kw |
| weight |
10000kg |
| cooling water |
16T/h |